Adipokines Regulate Insulin Sensitivity, Metabolic Processes, and Inflammation
Adipokines
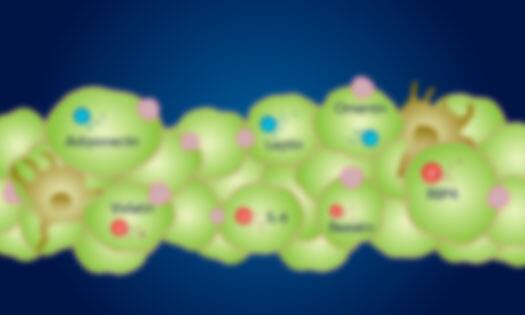
Adipokines are a group of bioactive peptides and proteins that are secreted by the adipose tissue. They act locally to promote autocrine and paracrine signaling, and peripherally to promote endocrine signaling. Proteins that are categorized as adipokines include leptin, adiponectin, chemerin, omentin, resistin, visfatin, and complement factor D/adipsin, among others. These factors play important roles in regulating a variety of metabolic processes, such as fatty acid oxidation, glucose uptake, lipogenesis, energy expenditure, and insulin signaling. Additionally, molecules such as IL-6, TNF-alpha, and VEGF are also classified as adipokines. They are secreted by either adipocytes or macrophages that infiltrate the adipose tissue and regulate processes such as inflammation, angiogenesis, and immune system functions. These proteins are also thought to play a role in adipose tissue dysfunction and defects in glucose metabolism.
Due to their abilities to influence insulin sensitivity and metabolism, changes in adipokine levels, may contribute to the pathogenesis of insulin-related metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Type 2 diabetes is characterized by a loss of insulin sensitivity that leads to an inability to properly regulate blood glucose levels. One of the leading risk factors for type 2 diabetes is obesity, a condition characterized by an excessive expansion of the white adipose tissue that occurs due to an increase in adipocyte size or number. This increased adiposity is coupled with a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation and altered adipokine secretion. The connection between obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes suggests that the molecular mechanisms behind these two conditions may be linked. As a result, the effects of adipokines such as leptin, adiponectin, resistin, chemerin, omentin, visfatin, FGF21, and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha, on insulin sensitivity and metabolic signaling pathways are being widely investigated. This research will lead to a greater understanding of how changes in adipokine secretion or crosstalk between different metabolic pathways may contribute to development of insulin resistance and the pathogenesis of metabolic disorders.
Bio-Techne offers a wide range of reagents for adipokine research. Our portfolio includes bioactive R&D Systems™ recombinant proteins for investigating the effects of different adipokines, conjugated and unconjugated R&D Systems™ and Novus Biologicals™ antibodies to analyze the expression of adipokines or adipokine receptors, and single and multi-analyte immunoassays for exploring the conditions under which adipokines are up-regulated or the effects of adipokines on other molecules.
Adipokines - Products by Molecule
Adipokines Regulate Metabolic Processes, Inflammation, and Angiogenesis

Adipokines Secreted by the Adipose Tissue Play a Central Role in Regulating Multiple Metabolic Processes, Inflammation, and Angiogenesis. Adipose tissue is an active endocrine organ that secretes peptide hormones collectively known as adipokines. These factors play a key role in regulating biological processes such as adipocyte differentiation, glucose and fatty acid metabolism, insulin sensitivity, inflammation, immune responses, and angiogenesis. As a result, changes in the circulating levels of adipokines can have deleterious effects and are thought to contribute to the development of metabolic disorders, such as type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
Bioactivity Testing of R&D Systems Recombinant Human Leptin

Leptin Stimulates Proliferation of the BaF3 Mouse Pro-B Cell Line. Baf3 mouse pro-B cells transfected with human Leptin R were treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human Leptin (R&D Systems, Catalog # 398-LP) and cell proliferation was assessed. The ED50 for this effect is 0.4-2 ng/mL.
Assessment of the Bioactivity of R&D Systems Recombinant Human PBEf/Visfatin

PBEF/Visfatin Induces VEGF Secretion by Human Prostate Cancer Cells. PC-3 human prostate cancer cells were treated with increasing concentrations of Recombinant Human PBEF/Visfatin (R&D Systems, Catalog # 8424-VF) and VEGF secretion was measured using the Human VEGF Quantikine™ ELISA Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # DVE00). The ED50 for this effect is 1-5 ug/mL.
Quantification of IL-6 Secretion in Untreated and Treated Primary Human Adipocytes

Quantification of IL-6 Secretion by Primary Human Adipocytes Following Treatment with TNF-alpha or sFRP-5 and TNF-alpha. Primary human adipocytes were either untreated (basal), treated with TNF-alpha alone, or treated with sFRP-5 (R&D Systems, Catalog # 6266-SF; 100 ng/mL; 4h) prior to incubation with TNF-alpha (5 nmol/L). IL-6 secretion was quantified using the Human IL-6 Quantikine ELISA Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # D6050). Figure from Carstensen, M. et al. (2014) PLoS ONE 9:e85906.
Simultaneous Detection of Multiple Adipokines Using the Proteome ProfilerTM Mouse Adipokine Array Kit

Detection of Adipokines in Cell Culture Supernatants from Undifferentiated and Differentiated Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast Cells Using the Proteome Profiler Mouse Adipokine Array. 3T3-L1 mouse embryonic fibroblast adipose-like cells were either undifferentiated or differentiated with methylisobutylxanthine (115 ug/mL), insulin (10 ug/mL), and dexamethasone (390 ng/mL) for 48 hours followed by the addition of insulin (10 ug/mL) for the next 48 hours. The cells were then grown in standard media for an additional 96 hours. Cell culture supernatants were removed and assayed using the Proteome Profiler Mouse Adipokine Array Kit (R&D Systems, Catalog # ARY013). Histogram profiles for select proteins detected in the cell culture supernatants of undifferentiated (gray bars) and differentiated (blue bars) cells were generated by quantifying the mean spot pixel densities from the arrays using image software analysis.
Featured Adipokine and Adipogenesis Products

StemXVivo™ Osteogenic/Adipogenic Base Media
StemXVivo™ Osteogenic/Adipogenic Base Media
Utilize our StemXVivo Osteogenic/Adipogenic Base Media and Adipogenic Supplement to efficiently and consistently drive the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into adipocytes. This defined media and supplement were specifically developed and optimized to induce adipogenesis in MSC cultures and reduce experimental variation.

Proteome Profiler Adipokine Arrays
Proteome Profiler Adipokine Arrays
The Proteome Profiler Human, Mouse, and Rat Adipokine Arrays offer a simple and inexpensive method to simultaneously analyze multiple analytes in a single sample, using chemiluminescence and standard Western blotting equipment. Utilize these multiplex membrane-base assays for your early stage adipokine discovery research.

Adipogenesis Markers
Adipogenesis Markers
Mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated in vitro into adipocytes, chondrocytes, or osteoblasts, which are then identified using antibodies against specific cell surface markers. Utilize our Pref-1 or FABP4 antibodies to detect either pre-adipocytes or mature, fully differentiated adipocytes, along with our wide selection of antibodies to analyze the expression of other adipocyte markers.
Featured Adipokine Resources

Adipokines and Insulin Signaling Pathway
Adipokines and Insulin Signaling Pathway
Adipokines are bioactive products secreted by the adipose tissue that can have pro- or anti-inflammatory effects and enhance or inhibit insulin signaling. As a result, they may contribute to the pathogenesis of insulin-related metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes. Explore the effects of different adipokines on insulin signaling using our interactive pathway.

Metabolic Syndrome Signaling Poster
Metabolic Syndrome Signaling Poster
Developed in collaboration with Dr. Robert H. Lustig, University of California and Dr. Alejandro Gugliucci, Touro University-California, this poster provides a tour of the signaling events involved in glucose and lipid homeostasis, while highlighting the molecular dysfunctions at the core of metabolic syndrome.

Adipokines and Metabolism
Adipokines and Metabolism
Adipokines are involved in regulating lipid metabolism, energy balance, and insulin signaling. Learn about our complete portfolio of products for studying lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and energy balance.
Leptin
Leptin binds to receptors in the hypothalamus stimulating the expression of genes associated with appetite suppression. In addition, leptin promotes catabolism and thermogenesis. Mice in which the leptin gene is disrupted (ob/ob mice) have traits that mimic many of the metabolic disorders associated with type 2 diabetes. These mice are obese, insulin resistant, and have an insatiable appetite. In contrast to leptin-deficient mice, obese individuals typically have elevated levels of leptin, presumably caused by a homeostatic attempt to compensate for a defect in the leptin signaling pathway. Elevated leptin levels are typically associated with a loss of leptin sensitivity.
Adiponectin
Like leptin, adiponectin is another polypeptide hormone that increases the sensitivity of target tissues to insulin. Reduced adiponectin levels are associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Both leptin and adiponectin stimulate the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which promotes fatty acid oxidation and glycolysis, and inhibits triglyceride, cholesterol, and fatty acid synthesis.
Visfatin
Visfatin was originally characterized as a nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase, an enzyme that is involved in the synthesis of nicotinamide mononucleotide from nicotinamide. Its enzymatic activity was also found to be required for the synthesis of NAD, an electron carrier that enables the synthesis of ATP. As an adipokine, visfatin was originally described to function as a non-competitive insulin-mimetic but has since been shown to induce insulin resistance in many tissues and to be involved in pancreatic beta cell dysfunction. Visfatin has been characterized as a pro-inflammatory cytokine and its levels are significantly increased in patients with type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular diseases.
Omentin
Omentin, also known as intelectin-1, is an anti-inflammatory adipokine that is primarily expressed in the visceral adipose tissue. It enhances insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and transport, and circulating levels are increased after weight loss. Omentin levels are negatively correlated with obesity and type 2 diabetes, and positively correlated with the levels of adiponectin and high density lipoprotein.
Chemerin
Chemerin is an adipokine that promotes adipocyte maturation. It can bind to three potential receptors (CMKLR1, GPR1, and CCRL2), but its primary receptor is CMKLR1. A number of studies have reported that chemerin affects insulin signaling and production, but some results have been contradictory, suggesting that it may have different effects in different tissues. In humans, multiple studies have shown a correlation of high levels of chemerin with obesity and insulin resistance. Chemerin is primarily considered to be a pro-inflammatory adipokine. It can recruit dendritic cells into visceral adipose tissue to promote inflammation and circulating levels of chemerin have been shown to positively correlate with the levels of IL-6, TNF-alpha, and C-reactive protein (CRP).
Serpin A12
Serpin A12, also known as vaspin, is expressed in both the visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue. Vaspin has been suggested to have an insulin-sensitizing effects based on the findings that it improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in obese mice fed a high fat and high sucrose diet. It was also found to increase insulin sensitivity and reduce food intake when administered to db/db mice, which serve as a model of type 2 diabetes. In humans, vaspin levels have been found to be increased in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes.